Capacity
The capacity of RAM modules is measured in megabytes, gigabytes and terabytes. For casual users, 4GB RAM is sufficient. Unlike gamers or heavy users, the most ideal RAM that users can buy is 8GB or larger so that he can be assured that he have enough space for his operating system as well as a resource-heavy game.
In other words, more is always better if users can afford it but have to beware that each system has a different limit for the maximum amount it can support. To find this out, check motherboard manufacturer’s website for the maximum amount of memory supported.

Frequency
RAM runs on various frequencies where its controller can perform a task using each “tick” of the RAM’s clock. The frequency is measured in MHz and higher numbers potentially indicate faster access to the information store in memory. Similarly, the higher the frequency, the better the performance, so it’s ideal to go as high as the system or motherboard supports. This information can be found in the same location as the maximum amount supported (mentioned above).
Please note that some motherboards list a few supported frequencies with (O.C) next to them. This means that those frequencies can be supported but the system needs to be overclocked to do so. Otherwise, if the memory that natively supports one of those frequencies and does not overclock the system, it won’t run at the RAM’s full potential frequency or even not at all.

Latency
Last but not least RAM also has various latencies for different tasks such as searching for a location in memory, reading the location, etc. Latency describes the delay between a request and execution of the task, meaning lower numbers are better. For example, latencies are usually described as “10-10-10-27”, which means that it has a latency of 9 memory clocks for one task, latency of 1 memory clock for another task and so on. There should be a total of four numbers. All motherboards should support all latencies as these describe the responsiveness of the RAM rather than how it interacts with the motherboard.
Together both frequency and latency affect the speed of RAM. A higher frequency, which makes RAM faster can compensate for higher latency, which makes RAM slower. Generally said, it is better to prioritize capacity over frequency and latency because more is always better.

How much do you need? Some guidelines
In a nutshell, here are some simple guidelines that apply to most PC devices.
- 2GB: Only really found in budget tablet designs. Fine for them, but you’ll want more in a laptop or desktop.
- 4GB: Entry level memory that comes with even budget notebooks. Fine for basic Windows and Chrome OS usage.
- 8GB: Excellent for Windows and MacOS systems and entry-level gaming.
- 16GB: Ideal for professional work and more demanding games. With RAM prices so low, this is the sweet spot for desktop users.
- 32GB and beyond: Enthusiasts and purpose-built workstations only.
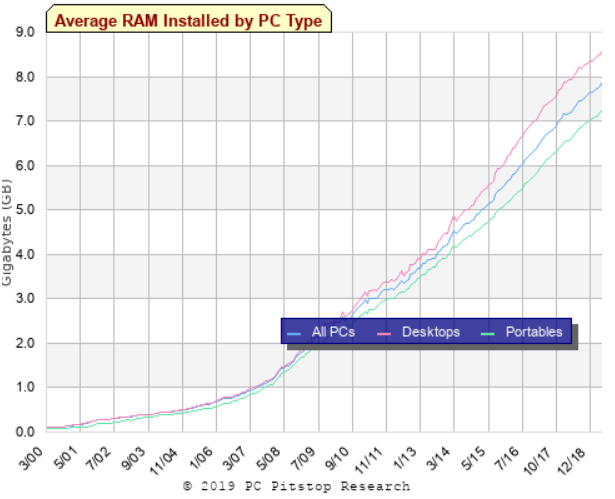
Average RAM Installed by PC Type in the past 17 years in which the amount of Gigabytes (GB) are getting higher
Remember, buying more RAM than you need doesn’t net you any performance benefit. It’s effectively wasted money. Buy what you need, and spend what’s left of your budget on more important components such as the CPU or graphics card.
Article Source: https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/how-much-ram-do-you-need/
Pingback: Bulk URL Shortener
Pingback: اول جامعة يمنية تدخل تصنيف التايمز
Pingback: مجلة جامعة الملكة أروى
Pingback: Queen Arwa University ROR ID: 03ygqq617
Pingback: Kuliah Mudah
Pingback: 918kiss
Pingback: porno izle
Pingback: cocuk porno